Question: - What is the relation between science and engineering?
Answer: - Science is about knowing and engineering is about doing. Science is synthesis of knowledge by understanding the law of nature, while engineering is the application of knowledge to transform the nature for serving people. Engineers use the scientific knowledge to build processes, structures and equipment. Both engineers and scientists have sound knowledge of science, mathematics and technology, but engineers are trained to use these principles in designing creative solutions to the challenges. Science is about studying what is existing, engineering is about creating, what never was. Science and engineering, both complement each other, for to transform nature effectively requires proper understanding, and to discover nature’s secrets requires instruments to modify it in experiments.
Question: - Why Biology is important for engineers?
Answer: - Biology may not be a typical subject in the traditional disciplines (i.e. civil, electrical, or mechanical), however, it is a fundamental component of disciplines such as biosystems engineering. Biosystems engineering emphasizes the application of engineering principles to biologically based systems.
Question: - What are the differences between Camera and Eye?
Answer: -
Differences between camera and human eye
CAMERA HUMANEYE
Focal length of lens is fixed Focal length of the lens be changed
Photographic film retains the Retina retains the impression of
Image permanently an image for only 1/16th second
A photograph has to be changed Same retina can be used viewing
For getting next image viewing unlimited images
Image is formed on photographic Image is formed on retina which
Film and processing can be done through is further processed in brain
Computer
__________________________________________________________________
Question: - What are the 4 principles of flight?
Answer: -
01 Lift: The force that pushes upward, created by the movement of air over and under the wings.
02 Drag: The force of the air pressing against the birds and slowing them down.
03 Thrust: The force that moves the bird forward, caused when a bird flaps its wings.
04 Propulsion: It means to push forward or drive an object forward. A propulsion system is a machine that produces thrust.
Newton’s Third Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. Thrust often comes from muscles or engines.
Question:- How do you proteins act as enzymes?
Answer: - Cells rely on thousands of different enzymes to catalyze metabolic reaction. Enzymes are proteins, and they make a biochemical reaction more likely to proceed by lowering the activation energy of the reaction, thereby making these reactions proceed thousands or even millions of times faster than they would without a catalyst. Enzymes are higher specific to their substrates. They bind these substrates at complementary areas on their surfaces, providing a snug fit that many scientists compare to lock and key. Enzymes work by binding one or more substrates, bringing them together so that a reaction can take place, and releasing them once the reaction is complete. In particular, when substrate binding occurs, enzymes undergo a conformational shift that orients or strains the substrates so that they are more reactive.
Question:- Describe proteins as structural unit?
Answer: - The building blocks of proteins are amino acids, which are small organic molecules that consist of an alpha (central) carbon atom linked to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a variable component called a side chain.
Proteins are the end products of the decoding process that starts with the information in cellular DNA. As workhorses of the cell, proteins compose structural and motor elements in the cell, and they serve as the catalysts for virtually every biochemical reaction that occurs in living things. This incredible array of functions derives from a startlingly simple code that specifies a hugely diverse set of structures.
In fact, each gene in cellular DNA contains the code for a unique protein structure. Not only are these proteins assembled with different amino acid sequences, but they also are held together by different bonds and folded into a variety of three dimensional structures. The folded shape, or conformation depends directly on the linear amino acid sequence of the protein.
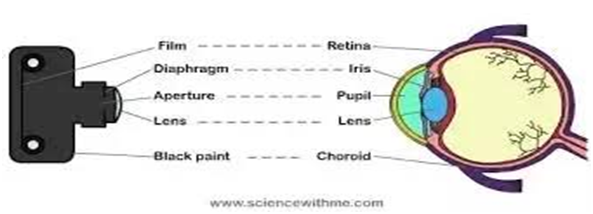
Question: - Similarities between camera and?
Answer: -
Similarities between camera and eye
Part of the Corresponding Function
Camera part of eye
____________________________________________________________________
Aperture Pupil ---------------- Light enters the eye through the
Pupil/aperture
Diaphragm Iris ----------------The iris/ diaphragm regulates the
amount of light entering the
eye /camera
lens Lens ---- Focus light and image on the
retina in eye and film in camera
Film Retina ------------------The part on which images are
formed
Black paint Choroid ------------------ The dark colored melanin
Pigment in the choroid and
black paint in the camera
absorbs light and limits
reflections within the eye that
could degrade vision
_________________________________________________________________
Question:- State the difference between Unicellular and Multicellular
Organisms?
Answer: -
Cellularity
An organism can be unicellular or multicellular. The number of
cells decides the structure, metabolic functions and other parameters of
organism. The characteristics of unicellular and multicellular are given bellow
.
Differences between unicellular and Multicellular organism.
Characteristics….Unicellular organis….Multicellular organism
Cell number Single cell Large number of cells
Function All function are Different cells perform
Performed by single cell different specific
functions
Division of labor Not performed Cells specified to perform
different functions.
Reproduction Involves the same Specialized cells, germ
Single cell cell take part in reproduction
Life span Short Long
__________________________________________________________________
Question:-Explain Mendel's law of segregation. Give an example.
Answer: -
Law of Segregation (First Law)
this law states that the alleles do not show any blending and both the characters are recovered as such in the F2-generation, though one of these is not seen in the F1-generation.
Due to this, gametes are pure for a character. The parents contain two alleles during gamete formation.
The factors or alleles of a pair segregate from each other such that a gamete receives only
|
Punnett squares to show height in F1 and F 2generations |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
T = tall plants t = short plants |
|
|||||||
|
F1 generation |
F2 generation |
|
||||||
|
|
T |
T |
T |
t |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
t |
Tt |
Tt |
t |
Tt |
Tt |
|
||
|
t |
Tt |
Tt |
t |
Tt |
Tt |
|
||
|
|
|
|||||||
|
|
100% Tt |
|
|
25% TT / 50% Tt / 25% tt |
||||
|
| ||||||||
(Fig.3.1) punnett squire showing law of segregation
Mendel’s discovered that, when he crossed tall pea plant with dwarf pea plant the result was in the F1 generation (offspring) all tall pea plant were produced. When Mendel self-fertilized the F1 generation pea plant, he obtained tall pea plants to dwarf pea plant ratio in the F2 generation 3:1.
Question:- Comparison between flying birds and aeroplane
Answer: Comparison between flying of aeroplane and birds
Function
part of the aeroplane
part of the birds
Lift
propellers/airfoil
Muscles
Drag
Streamlined shape
Light weight skeleton
and streamlined shape
Thrust
Movement of
aeroplane
Flapping of wings
and
wings by engine
Control
Wings
Tail and wing
Propulsion
Engine
Muscles



0 Comments